A domain name is the address that people use to access websites on the internet. It’s like your home address, but for websites. Instead of typing out long and complicated IP addresses, users simply enter a domain name like www.youtube.com to visit a website. Without domain names, navigating the internet would be much harder and less convenient.
The first-ever domain name registered was symbolics.com in 1985, and it’s still active today! Understanding how domain names work is important for anyone who plans to create a website. Domains are what make websites easily accessible and recognizable to users around the world. By knowing how they function, you can choose the right domain name for your own online presence.
Plus, with over 1.8 billion websites online today, having a memorable and clear domain name is more important than ever!
Table of Contents
What is domain?

Domain names are basically particular words that are used to visit someone’s website or your online unique identity. In a simple way, a domain name is just like an address for your website.
This internet world is like the normal world. Let’s say your best friend invites you to dinner at night and gives you the address of his house, and the address is XYZ, New Delhi, so now you have to go to that particular address (XYZ, New Delhi). There can be many people at the place, but the address will be particular or unique.

The same goes for the internet world; you might hear about IP address — each website has its unique IP, which cannot be driven to any other person till you are paying for that. What people search for you on a web browser’s URL bar is your internet address (domain).
How does domain work?
It is a little bit technical (but I made it as easy as I can, promise!). The internet you are using in your device is also using the servers that host your website, which has an IP address. It’s a number of 4-12 that is separated by dots (.) that actually identify each computer.
for example, here’s the IP address for Shivani Digital:
122.162.228.18

How to know your IP address? You can easily find out by just clicking here. For the machine, it’s easy to remember these 12 digital numbers for every website, but hard for human beings. That’s why domain names exist.
By domain name, you can easily remember the key phrase or phrases of the website name, like shivanidigital.com
Part of Domain Name
A domain name is made up of several components that come together to form a unique address for a website on the internet. Here’s an overview of the key parts:
- Top-Level Domain (TLD)
- Second Level Domain (SLD)
- Subdomain
- Domain Name Extension
TLD & SLD
This is the last part of a domain name, located after the final dot. Examples are:

- .com (commercial)
- .org (organization)
- .edu (education)
- .net (network)
- .gov (government)
Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the part of the domain name that comes just before the TLD.
Top-Level Domain (TLD) & Second Level Domain (SLD) is like a person’s name. For example, in person names—right at the end they use their family or surname and on the left at the first, they use their name, like. Shivani Digital (SLD) .com (TLD).
Subdomain
Subdomains appear before the second-level domain and are used to organize different sections of a website. For instance, in blog.example.com, “blog” is the subdomain. While not all domain names include subdomains, they are helpful for categorizing or adding specific functions to a site.
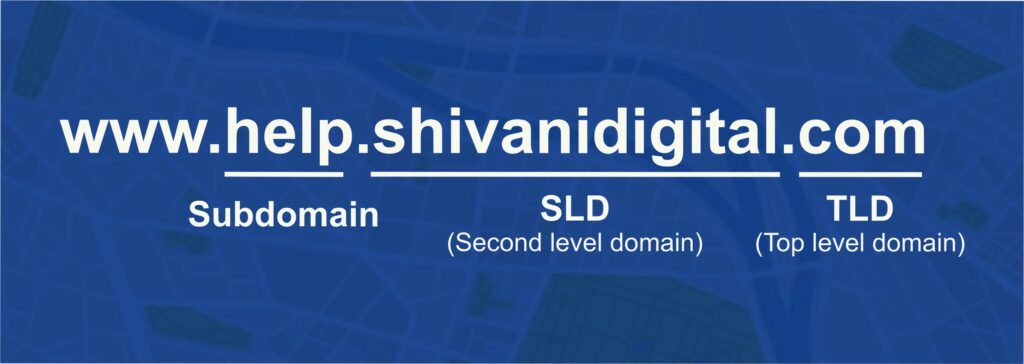
For example, you might have seen pages like “help.instagram.com” “help.facebook.com” – “help” is a subdomain now. They use subdomains for their separate pages (developers.facebook.com, help.instagram.com).
Domain Name Extension
This is the suffix that follows the second-level domain. It can include TLD, ccTLD, gTLDs.

(Country code top-level domain (ccTLD): You may have seen .in, .uk, .it, .ca It is basically a two-letter domain extension that stands for specific country, like .uk is the united kingdom and .in is for India).
(Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs): are designed to serve particular industries, communities, or purposes. These domain extensions allow businesses, organizations, or individuals to express their niche or focus directly through the domain name).
| TLDs | ccTLDs | gTLDs |
|---|---|---|
| .com | .in | .ai |
| .org | .us | .tech |
| .gov | .uk | .shop |
| .mil | .ca | .online |
| .net | .it | .store |
FAQs
What are the components of a domain name?
A domain name consists of the Top-Level Domain (TLD), Second-Level Domain (SLD), subdomain, and domain name extension. Examples include “.com”, “.org”, “.edu”, etc.
What are domain name extensions?
Domain name extensions are suffixes like .com, .org, .net, or country-specific extensions like .in for India. These help identify the type or origin of the website.



